As a coach, are you looking for effective coaching models to help your clients achieve their goals? With so many coaching models out there, how do you know which ones are truly effective and worth implementing in your practice?
In this article, we will explore nine proven coaching models that every coach should have in their toolkit.
In Brief : 9 proven coaching models that are a must-have for all coaches
- 🥇 GROW: Goals, Reality, Options, Will—a goal-oriented framework for identifying objectives, analyzing reality, exploring options, and committing to action.
- 🥈 STEPPA: Subject, Target, Emotion, Plan, Pace, Adapt—a holistic approach focusing on comprehensive goal achievement strategies.
- 🥉 CLEAR: Contracting, Listening, Exploring, Action, Review—emphasizes clear communication, exploration of ideas, and actionable steps towards goals.
- CIGAR: Current reality, Ideal reality, Gaps, Actions, Review—for gap analysis and creating a detailed action plan.
- OSCAR: Outcome, Situation, Choices/Consequences, Actions, Review—a solution-focused model for achieving specific outcomes.
- Solution-Focused: Prioritizes quick, positive changes by focusing on solutions rather than dwelling on problems.
- AOR: Awareness, Options, Results- emphasizes awareness and exploring options to achieve tangible results.
- FUEL: Frame, Understand, Explore, Lay Out—a structured conversation framework for understanding and planning success.
- WOOP: Wish, Outcome, Obstacle, Plan—a mental strategy focusing on overcoming obstacles to achieve goals.
What are Coaching Models
Whether you are an experienced coach or looking into starting your own coaching business, having a coaching model is a must-have. It makes you look credible and helps you refine your coaching practice.
A coaching model is an essential framework designed to help clients succeed and achieve their goals. It combines a coach’s unique methods with a set of strategic coaching tools to bolster the practice’s effectiveness and credibility.
These models use a systematic approach. They provide a structured way for clients to develop. This includes defining goals, exploring perspectives, and making actionable plans.
Research shows that coaching using psychology makes a big difference. It uses ideas from psychotherapy and positive psychology. This can improve learning outcomes. These include feelings, thinking, skills, performance, and mental health.
These methods offer a complete view of clients. They consider clients’ motivations, histories, and current situations. This helps clients make lasting changes in their behavior.[1]
This systematic framework makes coaching practices solid. It is based on established principles. This increases their effectiveness and reliability. It helps people reach their personal and professional goals.
Types of Coaching Models
Coaching models provide a structured framework that helps coaches work effectively with clients to reach goals and improve skills. There are various types of coaching models. Each model has its own unique approach and focus.
Here, we will explore some of the most widely used coaching models that you can utilize to enhance your coaching practice.
- 🥇 The GROW Coaching Model: Best For Personal Development
- 🥈 The STEPPA Coaching Model: Best For Enhancing Emotional Intelligence
- 🥉 The CLEAR Coaching Model: Best For Fostering Leadership
- The CIGAR Coaching Model: Best For Strategic Planning
- The OSCAR Coaching Model: Best For Executive Development
- Solution-Focused Coaching Model: Best For Crisis Intervention & Change Management
- AOR Coaching Model: Best For Team Development
- FUEL Coaching Model: Best For Personal Growth And Educational Development
- WOOP Coaching Model: Best For Motivational And Health & Wellness Enhancement
1. The GROW Coaching Model: Best for personal development
The GROW Coaching Model is a favorite tool for coaches everywhere. It was made by Sir John Whitmore and works like a map to help coaches and their clients navigate through coaching sessions. Think of it as going on a journey with four stops.
This model is great. It really helps coaches have important conversations with clients. It focuses on setting goals, understanding the current situation looking at different choices, and getting ready to act. This makes coaching more organized and effective.
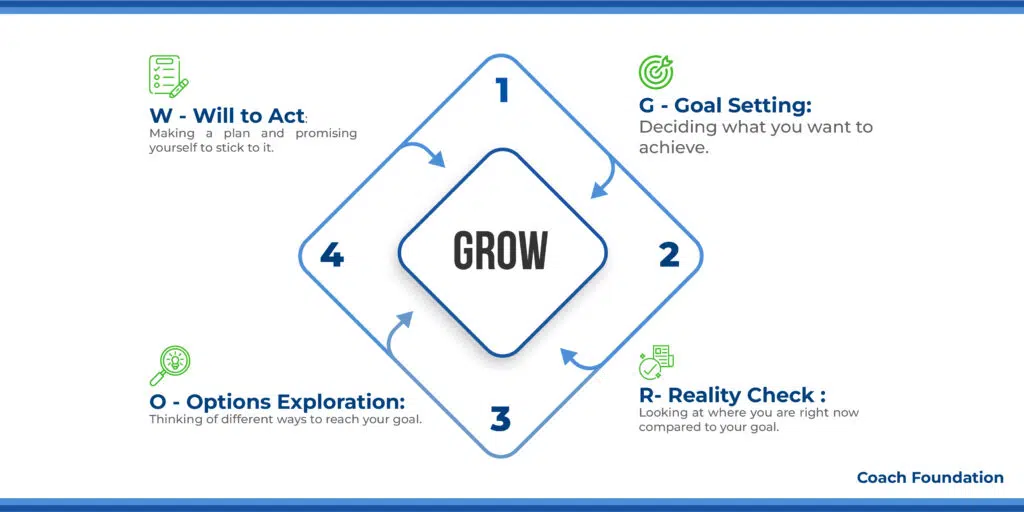
G – Goal Setting: This is where the magic starts. Coaches get down to brass tacks with clients, helping them figure out what they really want to hit in the next few months.
Coaches use goal setting exercises to help clients define objectives. These goals are actionable and aligned with their values and aspirations.
They could throw out active questions like, “What’s your big dream for the next quarter?” or whip out some handy goal-setting sheets to get everything down in black and white. It’s all about getting that target in clear view so clients know exactly where they’re aiming.
R – Reality Check: Next up, coaches help clients take a good, hard look at where they’re at right now. It’s like taking stock of your current situation with questions like, “How close are you to your goal right now?”.
Tools like a SWOT analysis are also used to really dive deep into what’s working, what’s not, and where the golden opportunities lie. It’s a crucial step to figure out the lay of the land and how to use what you’ve got to your advantage.
O – Options Exploration: Here’s where the brainstorming fun happens. Coaches nudge clients to think outside the box. Asking stuff like, “What are all the ways you could tackle this hurdle?”
Either by brainstorming or using decision-making tools, the goal is to generate multiple options. Using decision-making tools, the aim is to light up as many options as possible. Seeing all the different routes to the goal can really open up a world of possibilities.
W – Will to Act: Finally, we’re talking commitment. Coaches help clients lay down a solid game plan, asking the real questions like, “What’s your move, and when are you going to make it?” Using action plans or even commitment contracts can make those plans stick.
It’s also about looking ahead, figuring out what might trip you up, and how to leap over those hurdles. Getting down to the nitty-gritty of specific actions and deadlines clearly prepares clients. Keeping them on track to cross that finish line.
2. The STEPPA Coaching Model: best for Enhancing emotional intelligence
The STEPPA Coaching Model is a powerful approach for coaches who want to build a successful coaching career. It consists of seven key steps, each crucial for guiding clients effectively.
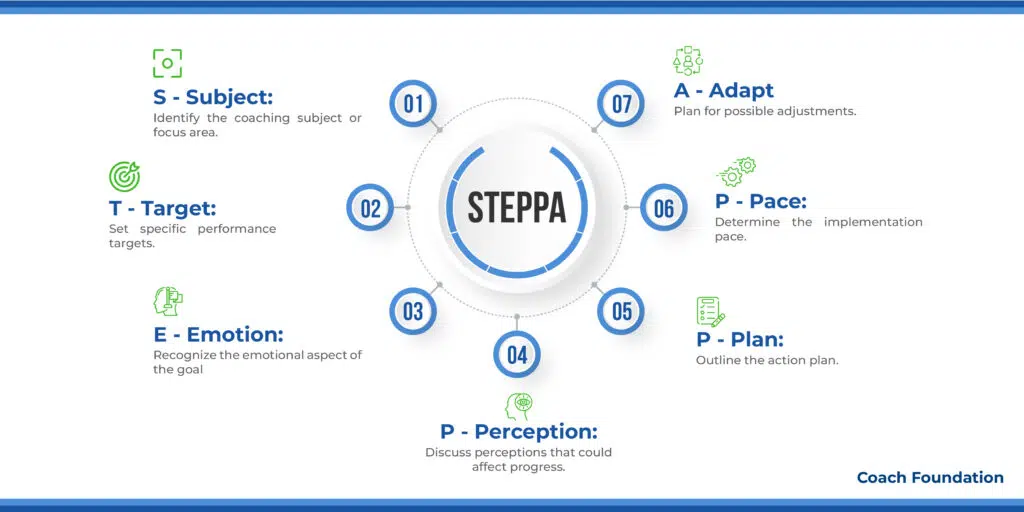
S – Subject: The journey starts with defining the focus. Coaches use focus area worksheets to help clients pinpoint their main goals or challenges. This ensures the coaching sessions are laser-focused on what the client wants to achieve or overcome.
This step is super important. It helps you keep things real and genuine with your clients, steering clear of any biases that could sneak into your sessions.
T – Target Setting: Setting clear, achievable targets is next. This could involve using SMART goal criteria to frame their objectives.
You could ask questions aimed at identifying ambitions, such as “What’s your major goal for the next six months?”. It will ensure that clients have a laser-focused aim for their efforts. It’s all about giving direction and purpose.
E – Emotion: Goals aren’t just about actions; they’re about feelings too. Emotion mapping tools allow clients to explore and express how they feel about their goals. This step is crucial for understanding motivation and addressing any emotional hurdles.
This process of self-discovery can lead to powerful insights and shifts in perspective, laying the groundwork for meaningful change.
P – Perception: How clients see the world can affect their progress. Perception challenge exercises help clients question and adjust any limiting beliefs or attitudes. This encourages a mindset that supports their goals rather than hindering them.
P – Planning: Working together, coaches and clients craft a detailed action plan. This involves breaking down larger goals into smaller, more manageable steps. Utilizing tools like action brainstorming worksheets helps to map out these steps along with deadlines, providing a clear path forward for achieving set goals.
P – Pace: Everyone moves at their own speed. Progress pacing guides assist in setting a realistic timeline that fits the client’s life. It’s about making consistent progress without feeling overwhelmed, ensuring the journey is sustainable.
A – Adapt: Flexibility is key. Adaptability planning tools prepare clients for the unexpected, helping them stay on course even when challenges arise. This builds resilience and ensures clients can adjust their plans while keeping their eyes on the prize.
This helps clients stay focused on their goals. Helping them remain motivated, especially when facing obstacles.
3. The CLEAR Coaching Model: best for fostering leadership
The CLEAR Coaching Model, created by Peter Hawkins, outlines a structured framework to boost coaching and mentoring effectiveness. It’s divided into five key phases.
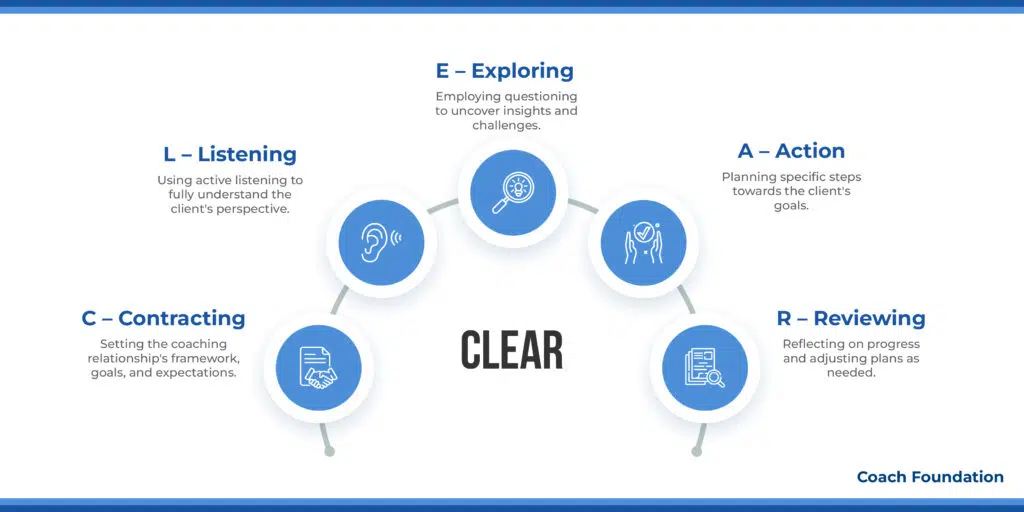
C – Contracting: This is where the ground rules are laid down. It’s a heart-to-heart between coach and client about what they’re aiming for, the dos and don’ts, and what’s expected from both sides.
Maybe you’ll use a coaching agreement or a chat about goals and what gets the client pumped. Asking something like, “What’s your big dream with our sessions?” can clear the air about what the client is after. The whole idea is to get on the same page so the journey’s smooth sailing, making every session count.
L – Listening: A cornerstone of effective coaching is the ability to listen. Active listening helps the coach understand the client’s thoughts and feelings. This can mean repeating their words or asking questions to show empathy.
The goal is to create a safe and trusting space. This way, the client feels seen and heard, which is key for good communication.
E – Exploring: At this stage, powerful questioning by the coach aids the client in gaining insights and self-awareness.
Questions such as, “What challenges are you facing in reaching your goal?” or “How do your beliefs impact your actions?” stimulate deep reflection.
The goal is to uncover issues or beliefs that are blocking the client’s progress. This lets them see things differently and find solutions.
A – Action: This is the phase where planning turns into commitment. The coach supports the client in developing SMART goals and actionable steps toward achieving these goals. Utilizing tools like action planning templates can organize this process.
Discussing, “What specific steps will you take this week towards your goal?” encourages the client to commit to tangible actions. The goal is to transition the client from contemplation to action, promoting advancement and growth.
R – Reviewing: The last leg of the journey’s about taking stock—looking back at the ground covered, the hurdles jumped, and the wins along the way. Review sessions might dive into achievements, hiccups, and how tough spots were tackled.
Questions like, “What lessons are you taking from your efforts?” or “How should we tweak our game plan to better chase your goals?” help celebrate the victories and fine-tune future strategies.
It’s about keeping the momentum going and encouraging a mindset that’s all about growing and evolving.
4. The CIGAR Coaching Model: Best for Strategic planning
The CIGAR Coaching Model by Suzy Green and Anthony Grant places a strong emphasis on the client’s present reality and focuses on helping them gain clarity and awareness about their current situation.
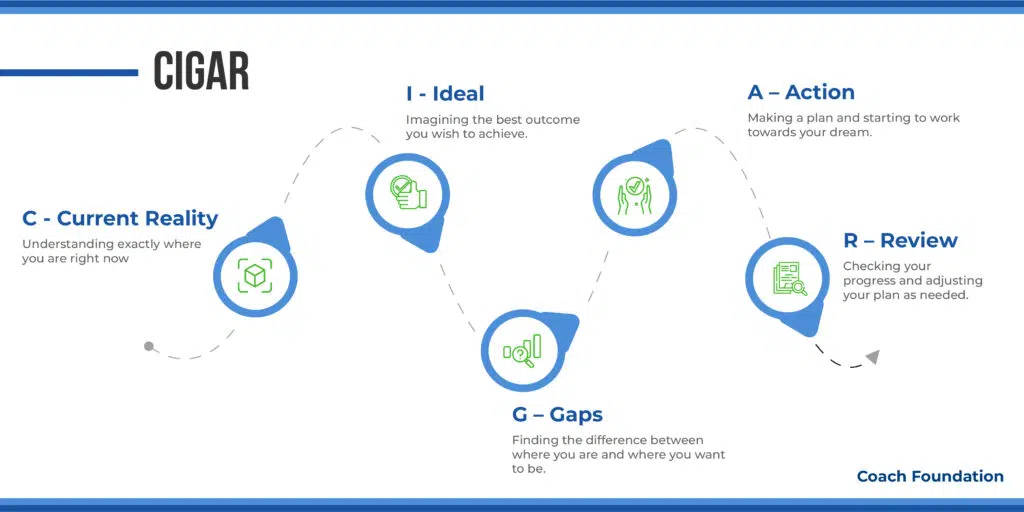
C – Current Reality: Off the bat, it’s about getting the full picture of where the client stands today. Using tools like the Wheel of Life to peek into different areas of the client’s life or popping questions like, “What’s tripping you up these days?” aims to sketch out a detailed landscape of the client’s current scene—challenges, strengths, and all. This snapshot is key because it lays the groundwork for everything that comes next.
I – Ideal: Here, the focus shifts to what the client wants to achieve—their vision for the future. Coaches could encourage clients to create a vision board or use guided imagery exercises.
Questions like, “What does success look like for you?” help clients articulate their goals, aspirations, and desired outcomes clearly. This step serves to motivate and direct the client’s efforts by establishing a clear destination.
G – Gaps: Identifying the discrepancies between the client’s current reality and their ideal future is the essence of this phase. Coaches can use SWOT analysis or ask, “What obstacles are currently standing in your way?”
This phase is vital for understanding what needs to change or improve, helping the client and coach pinpoint focus areas for action.
A – Action: This step is where planning meets execution. Crafting a step-by-step game plan with the client turns all those insights and dreams into a to-do list. Tools such as action planning templates or setting SMART goals are instrumental here.
Discussing questions like, “What is one step you can take this week towards your goal?” helps translate the client’s aspirations into actionable tasks. This step is critical for momentum, turning the client’s vision and insights into tangible progress.
R – Review: Keeping tabs on how things are going is a must for tweaking and cheering on progress. Whether it’s through regular catch-ups or moments of reflection with questions like, “How close are you to hitting your target?” ensures the coaching journey stays flexible and attuned to the client’s shifting needs.
This continuous loop of feedback and adjustment keeps the journey fresh and forward-moving.
5. The OSCAR Coaching Model: Best for executive development
Mark McKergow and Paul Z. Jackson created the OSCAR coaching model. This is broken down into five steps. Each step is designed to facilitate clear progression and actionable results. It focuses on establishing clear goals and objectives for the coaching session.
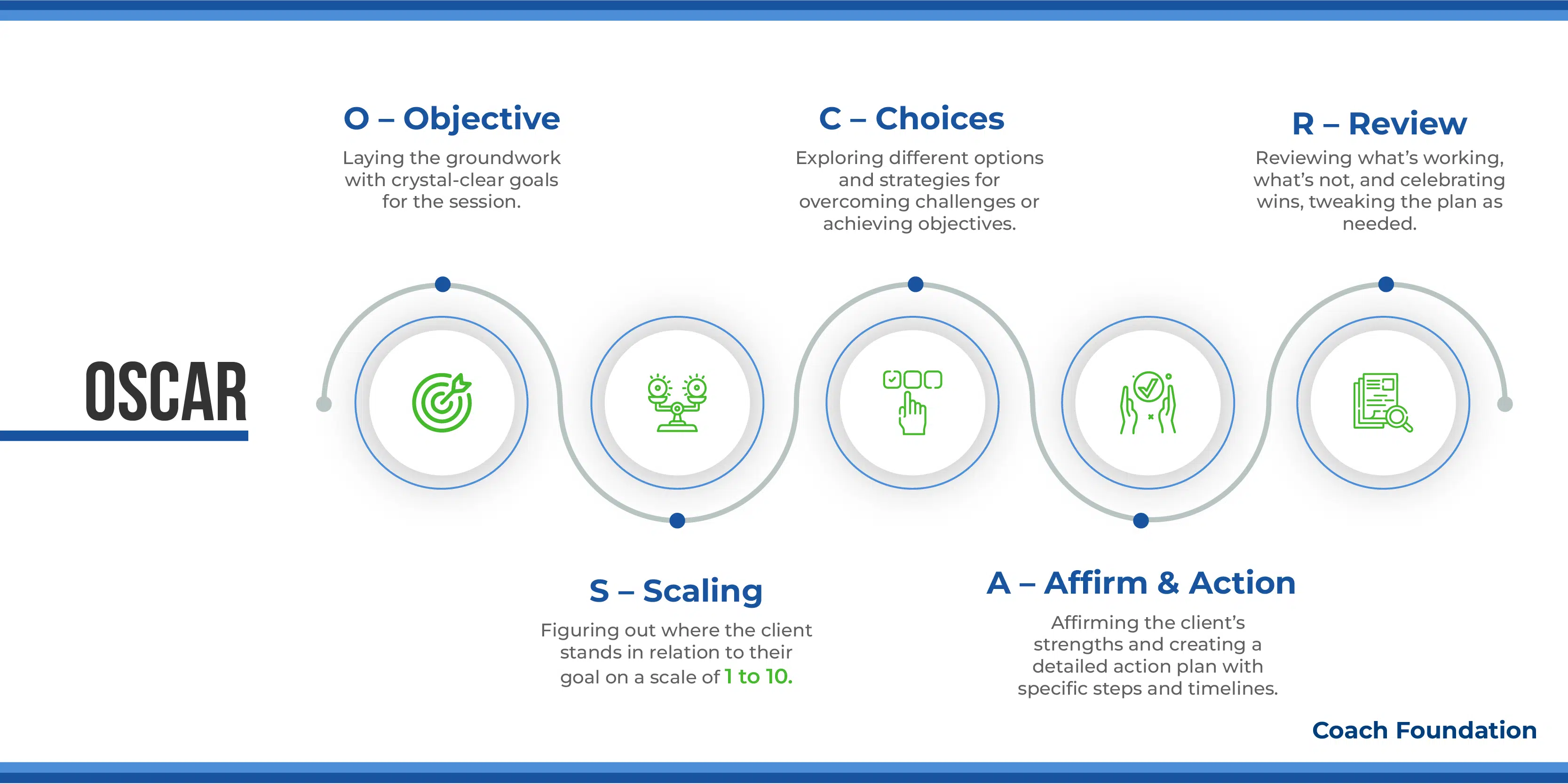
O – Objective: First off, we lay the groundwork with some crystal-clear goals for the session. Coaches might pull out a goal-setting template or just straight-up ask, “What’s the main thing you want to nail down today?”
This step makessure everyone’s on the same page and sets the stage for everything that follows. It’s like setting the GPS before you hit the road—knowing where you’re headed is key.
S – Scaling: Next, the coach figures out where the client stands in relation to their goal on a scale of 1 to 10. Asking something like, “On a scale of 1 to 10, how close do you feel you are to your goal right now?” helps put things into perspective.
It shows how far they’ve come and how far they’ve got to go. It’s a great way to make the journey toward the goal feel more tangible and trackable.
C – Choices: This stage is dedicated to exploring different options and strategies for overcoming challenges or achieving objectives. Coaches encourage clients to consider various approaches. They ask, “What different strategies could you employ to move from your current position to a higher number on your scale?”
This part’s all about opening up a world of possibilities and letting the client see all the different paths they could take. It’s a boost to their problem-solving muscles and gets them committed to the plan they choose.
A- Affirm & Action: Coaches affirm the client’s strengths and past successes to boost their confidence. They use affirmations like, “Let’s look at the strengths you’ve leveraged successfully in the past.” This is followed by creating a detailed action plan.
The conversation then shifts to defining specific steps, setting timelines, and agreeing on milestones with questions such as, “What is the first step you will take towards your goal, and by when?” This approach ensures the client feels supported and has a definitive strategy for moving forward.
R – Review: Rounding things off, the OSCAR model wraps up with a good old review session. Asking, “How’s the plan been treating you on your way to your goal?” will help coaches and clients get to dive into what’s working, what’s not, and celebrate the wins along the way.
This reflection time is golden for tweaking the game plan as needed. Making sure the coaching stays right on track with the client’s growth and successes. It keeps the whole process fresh and forward-moving.
6. Solution-Focused Coaching Model: Best for Crisis Intervention & Change Management
The Solution-Focused Coaching Model flips the script from zeroing in on problems to dreaming up solutions. Developed by Steve de Shazer, Insoo Kim Berg, and colleagues at the Brief Family Therapy Centre, in Milwaukee Wisconsin, USA. This model is targeted for clients with big visions.
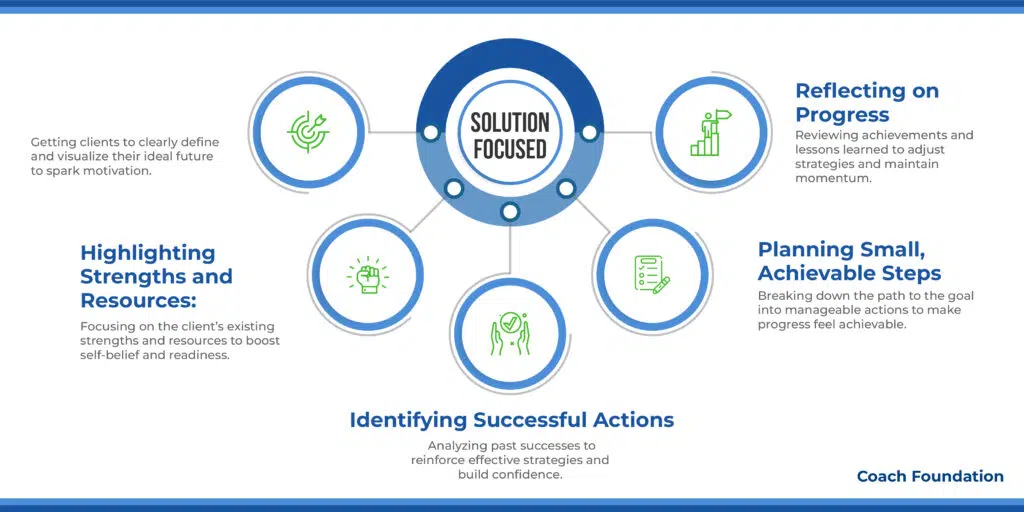
Envisioning the Future: Coaches kick things off by getting clients to dive deep into what they’re gunning for. Asking, “What’s your dream scenario?” or “How will you know you’ve hit your target?” gets clients to define what they’re really after.
Using vision boards or future scripting as well can help make these dreams feel more real. The goal here is to spark a hefty dose of motivation by setting a clear and upbeat direction.
Highlighting Strengths and Resources: This step’s all about spotlighting what the client brings to the table—their ace cards and the goodies in their toolkit. Coaches might ask, “What superpowers do you have that’ll help you on this quest?” or “What’s in your arsenal that’s helped you out before?”
This bit reinforces the idea that clients have what it takes to tackle their hurdles head-on, boosting their self-belief and shining a light on their toolkit for the adventure ahead.
Identifying Successful Actions: Digging into what’s worked in the past is key. By asking, “When were you a step closer to your goal, and what was your move?” or “What’s a win you’ve had recently?” clients start to see the patterns in their successes.
This step is a big high-five to the client’s ability to make good stuff happen, pumping up their sense of empowerment and the realm of what’s possible.
Planning Small, Achievable Steps: Here’s where the big dreams get broken down into bite-sized, doable deeds. Coaches might say, “What’s one tiny step you can take this week toward that big dream?” or use action planning sheets to sketch out the journey.
This approach turns the grand vision into a checklist of wins, making the whole thing feel a lot less daunting and a lot more doable.
Reflecting on Progress: Stepping back to see how far they’ve come and tweaking the game plan as needed is part of the ride. Questions like, “How much closer are you to your dream?” and “What’s a lesson you’ve picked up along the way?” give props for the progress made and the wisdom gained.
This regular reflection keeps the growth mindset in full gear. Encouraging them to pivot their strategies when necessary.
7. AOR Coaching Model: Best for Team Development
The AOR coaching model places a strong emphasis on the relationship between the coach and client. It focuses on the trial-and-error problem-solving method. It trains people to solve problems efficiently with few mistakes.
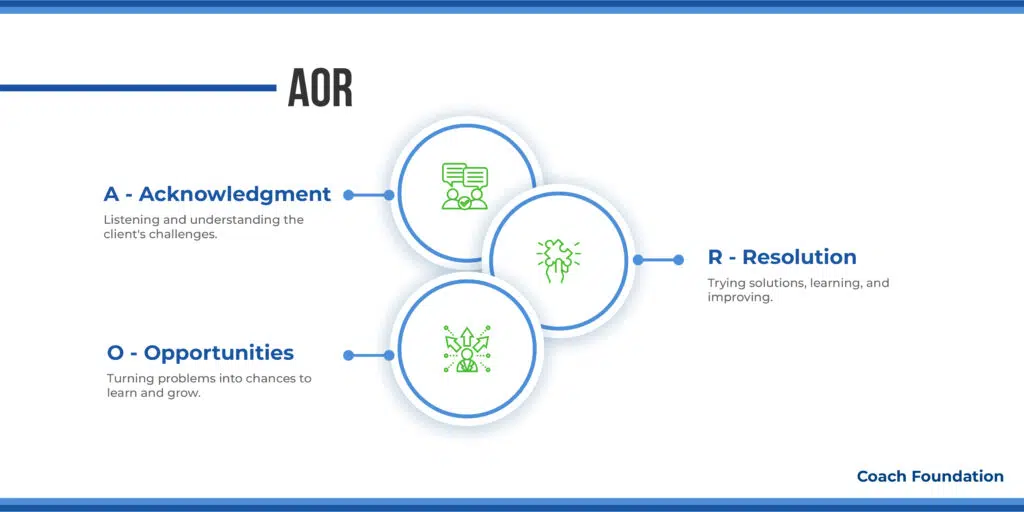
A – Acknowledgment: First things first, it’s about recognizing and getting the full picture of the hurdles the client is jumping over. Coaches are all ears, using their best active listening skills to really get where the client is coming from.
They could ask, “What’s the big challenge for you right now?” to make sure the client feels truly listened to and understood. The goal is to lay down a foundation of trust and open lines of communication, creating a solid base for everything that follows.
O – Opportunities: After shining a light on the challenge, it’s time to pivot to spotting chances for learning and growing. This step is all about flipping the script on setbacks and encouraging the client to see them as opportunities in disguise.
Questions like, “What’s the silver lining here?” or brainstorming sessions to map out different game plans help the client shift gears from problem-mode to opportunity-hunting mode.
R – Resolution: Now, we get into the nitty-gritty of trying stuff out and learning on the go. It’s all about embracing the try, fail, adjust, repeat cycle, with the coach throwing out questions like, “What’s one thing you can try out and see how it goes?”
Action plans and feedback loops come in handy here. The aim is to make the client confident and smart in handling challenges. They will use their learned lessons and improve their methods for better results.
8. FUEL Coaching model: best for Personal Growth and Educational Development
The FUEL coaching model places a strong emphasis on skill development and performance improvement.
Developed by John Zenger and Kathleen Stinnet, FUEL model consists of four key components. Let’s go over these:
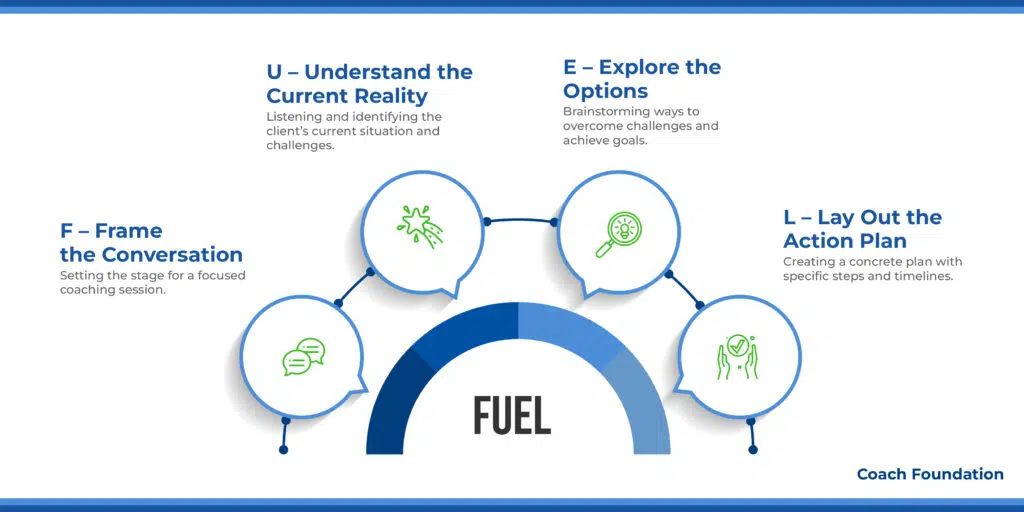
F – Frame the Conversation: Right out of the gate, it’s all about getting the scene set for a killer coaching session. Coaches lay down what’s on the agenda and whip up a space where everyone feels comfortable sharing.
They might kick things off with goal-setting exercises or setting the scene for what these sessions are all about. Asking questions like “What’s on your wish list for our time today?” The goal here is to get crystal clear on what we’re after, making sure both of you are in sync.
U – Understand the Current Reality: First, the coach needs to understand the client’s current situation. This includes all of their challenges. The coach listens carefully and asks direct questions.
For example, they might ask, “What’s causing problems in your work?” They might also use a SWOT analysis. This helps to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. The goal is to create a complete overview of the client’s situation.
E – Explore the Options: Coaches get clients to throw all sorts of ideas on the table about how to leap over their hurdles or hit their targets. Nudging them with, “How could you level up in this area?” or facilitating some out-of-the-box thinking sessions.
It’s all about dialing into their strong suits, peeking at things from a fresh angle, and laying out a game plan to tackle any obstacles head-on.
L – Lay Out the Action Plan: This is where all the brainstorming and strategizing come together into a solid game plan. Coaches and clients huddle up to nail down the exact steps, using action plan templates to make it all tangible.
Asking, “What steps are we taking first?” and setting dates make the plan real and possible.This step transforms all those good intentions into a legit roadmap.
9. WOOP Coaching Model: Best for Motivational and Health & Wellness Enhancement
The WOOP Coaching Model was developed by Gabriele Oettingen. The WOOP Coaching Model stands for Wish, Outcome, Obstacle, and Plan.
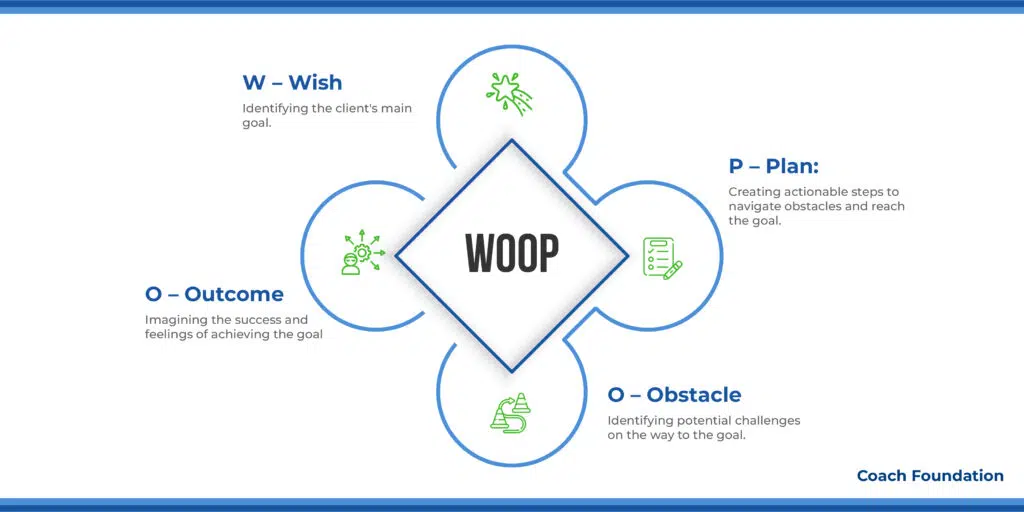
W – Wish: This initial step involves identifying the client’s goal or what they hope to achieve. Coaches might use visioning exercises or ask direct questions like, “What is your main goal for the near future?”
The game plan here is to get the client’s goals sharp and in focus, lighting the path for all the energy and hustle they’re about to pour into this dream. Nailing down this wish is all about getting that motivation dialed in just right.
O – Outcome: Next up, it’s time to get the client to really feel and see what snagging their goal looks like. You could guide them through some mental victory laps or ask, “How’s it going to feel when you’re living your goal?”
This step is all about sparking those happy feelings and the buzz of nailing it, which are huge cheerleaders in the goal-chasing race.
O – Obstacle: Here’s where we get real and scout out the rough patches on the road ahead. Tossing out a question like, “What speed bumps might pop up on your way to your goal?” or getting down to some forward-thinking troubleshooting helps the client spot potential snags early.
This foresight equips the client to approach challenges with a strategic mindset, enhancing their preparedness and resilience.
P – Plan: The final component focuses on developing specific, actionable strategies to overcome identified obstacles and advance towards the goal. With implementation intentions in the spotlight, you might dive into, “What’s your game plan for dodging those roadblocks?”
This part of the process is crucial for turning those big dreams into step-by-step actions.
Who can use these coaching models?
Coaching models are tools for growth and success. They fit anyone who leads, supports, or inspires others. These models make communication, problem-solving, and development easier. Professionals in leadership positions and coaches can use these coaching models.
Managers
Managers use coaching models to lead better. They help teams grow and solve problems. Managers learn to listen, ask good questions, and guide workers to success.
HR
HR professionals use coaching models to support employees. They help with career growth, learning, and solving work issues. HR can build a stronger company culture and improve staff happiness.
Coaches
And, of course, coaches use these models to help people. They guide clients to achieve goals, change behaviors, and improve skills. Coaches use questions and activities to inspire change.
Do I need to include a coaching model in my practice?
Incorporating a coaching model into your practice is more than just a structured approach. It’s foundational for fostering accountability and clarity with your clients.
- Laying out a clear plan ensures you and your clients are aligned on goals and objectives from the start.
- A coaching model also sets clear expectations. When clients understand the coaching journey and anticipated outcomes, it reduces uncertainty. This builds a trust-based coaching relationship.
- A coaching model creates an optimal learning environment for clients. A structured framework for their sessions makes clients feel supported and secure. This supportive, collaborative environment is crucial for fostering growth and achieving impactful results.
Integrating a coaching model into your practice may seem like an extra step. But, it’s a strategic move that greatly improves your coaching effectiveness and benefits both you and your clients
This is where we come in. Now that you have a solid knowledge base on coaching models, the next step is to integrate it into your coaching practice. We’ll also give you access to tools, strategies, and insights that will help you refine your coaching approach. This will ensure that your clients feel more empowered and supported than ever before.
Conclusion
There you have it—all the widely used coaching models listed under one roof.
It is an extensive, but not exhaustive, list of coaching models.
Ultimately, the choice of a coaching model—or models—reflects a coach’s dedication to providing tailored, effective support to their clients. Using a coaching model will help bring about meaningful and sustainable change in their clients’ lives.
Resources
Now that you have a good understanding of the coaching models, this resources section offers a curated collection of books, apps, podcasts, videos, and templates for continuous learning.
Each resource has been selected to complement the coaching frameworks discussed in the article, providing deeper insights, practical tools, and diverse perspectives.
A Few Other Coaching Models
- Arrow Coaching Model: focuses on direct, goal-oriented strategies where progress and success are aimed towards a specific target.
- Spiral Coaching Model: combines practical techniques with principles based on psychology and sociology to create long-term change outcomes.
Books
- “Coaching for Performance” by John Whitmore: A definitive guide to the GROW model and coaching principles.
- “The Coaching Habit” by Michael Bungay Stanier: Offers simple, effective tools for transforming coaching conversations.
Apps
- Coach.me: A habit-tracking app that supports goal setting and personal development. With its user-friendly interface and tailored approach, Coach.me assists users in developing new habits or breaking old ones by providing personalized tracking, reminders, and weekly progress report
- Hive: Hive is a comprehensive goal tracking app ideal for boosting productivity and team collaboration. With features like Hive Goals, users can set and visualize progress towards their objectives, whether individual or team-based. The app offers seamless integration with various tools and platforms, making goal management efficient and effective.
- Todoist: Todoist is a task management app designed to streamline workflow and declutter the mind by organizing tasks into to-do lists. It offers flexibility and ease of use, allowing users to view tasks for the day or the upcoming week
Templates
- Coaching session plan templates: Structured outlines for coaching sessions.
- Goal-setting templates: Tools to help clients define and track their goals effectively.
Worksheets
- Goal Development Worksheet: This valuable resource from Stony Brook University is essential for coaches guiding their clients through the goal-setting process. It facilitates breaking down aspirations into actionable steps, ensuring focus and progress towards success.
- Building New Habits: Making new habits isn’t hard if you start small and stay consistent. Utilize this worksheet as a coach to help your clients implement incremental changes that will lead to significant improvements in their lives.
References
- Wang, Q., Lai, Y.-L., Xu, X. and McDowall, A. (2022), “The effectiveness of workplace coaching: a meta-analysis of contemporary psychologically informed coaching approaches”, Journal of Work-Applied Management, Vol. 14 No. 1, pp. 77-101. https://doi.org/10.1108/JWAM-04-2021-0030
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What Is A Coaching Model?
A coaching model is a model or framework to help you, as the coach, guide your client to their desired results. The model is a source of inspiration, a reference tool, and a blueprint for your coaching work.
What are the 4 coaching models?
The GROW, STEPPA, CLEAR, and OSCAR models are examples of four coaching models, each offering unique frameworks for goal setting, action planning, and client development.
What are the 4 types of coaching?
The four types of coaching include Executive Coaching, Life Coaching, Sports Coaching, and Business Coaching, each focusing on different aspects of personal and professional development.
What is the most effective coaching model?
Effectiveness varies by context, but the GROW model is widely regarded for its simplicity and effectiveness in setting goals, understanding reality, exploring options, and committing to action.
What is the basic model of coaching?
The GROW model is considered a basic and foundational coaching model, focusing on Goal setting, examining the current Reality, exploring Options, and determining the Will to act.

ABOUT SAI BLACKBYRN
I’m Sai Blackbyrn, better known as “The Coach’s Mentor.” I help Coaches like you establish their business online. My system is simple: close more clients at higher fees. You can take advantage of technology, and use it as a catalyst to grow your coaching business in a matter of weeks; not months, not years. It’s easier than you think.
AS SEEN ON
0 Comment